概述
在jpaas 平台中,微服务的认证和授权的实现方式,采用了统一接入的机制,之后系统的接入都需要遵循这套机制来实现。
平台的安全认证是基于Spring Security 5 上实现的认证,一旦用户登录完成后,会把用户信息进行相应的存储,以方便后面的不同的微应用进行使用,那么网关如何知道当前用户登录已经登录了,并且可以访问哪些应用与哪些功能。

【说明】
平台中的角色如下
前端应用
前端负责从从后端获取数据,在前端进行展示。网关
负责请求转发,负载均衡,限流,检查TOKEN是否合法认证服务器
负责认证用户,分发访问令牌微应用
最终的数据返回者,微应用需要负责token是否有权限访问接口,另外如果通过feign 访问访问其他的微服务的时候,为了性能考虑,就不要在进行授权认证了。
安全管理配置入口
平台是由网关统一对外访问的,因此网关承担所有的访问的入口的安全拦截的第一道关口,因此所有的访问均需要通过网关进行转发,因此,我们配置了Spring Securityr的 安全拦截串。
package com.redxun.gateway.config;import com.redxun.gateway.auth.*;import com.redxun.oauth2.common.properties.SecurityProperties;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;import org.springframework.security.authentication.ReactiveAuthenticationManager;import org.springframework.security.config.web.server.SecurityWebFiltersOrder;import org.springframework.security.config.web.server.ServerHttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.TokenStore;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.resource.web.server.ServerBearerTokenAuthenticationConverter;import org.springframework.security.web.server.SecurityWebFilterChain;import org.springframework.security.web.server.authentication.AuthenticationWebFilter;import org.springframework.security.web.server.authentication.ServerAuthenticationEntryPointFailureHandler;/*** 资源服务器配置** @author yjy* @date 2019/10/5* <p>*/@Configurationpublic class ResourceServerConfiguration {@Autowiredprivate SecurityProperties securityProperties;@Autowiredprivate TokenStore tokenStore;@Autowiredprivate PermissionAuthManager permissionAuthManager;/*** Spring Security的安全认证配置入口** @param http* @return*/@BeanSecurityWebFilterChain springSecurityFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) {//认证处理器ReactiveAuthenticationManager customAuthenticationManager = new CustomAuthenticationManager(tokenStore);JsonAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new JsonAuthenticationEntryPoint();//token转换器ServerBearerTokenAuthenticationConverter tokenAuthenticationConverter = new ServerBearerTokenAuthenticationConverter();tokenAuthenticationConverter.setAllowUriQueryParameter(true);//oauth2认证过滤器AuthenticationWebFilter oauth2Filter = new AuthenticationWebFilter(customAuthenticationManager);oauth2Filter.setServerAuthenticationConverter(tokenAuthenticationConverter);oauth2Filter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(new ServerAuthenticationEntryPointFailureHandler(entryPoint));oauth2Filter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(new Oauth2AuthSuccessHandler());http.addFilterAt(oauth2Filter, SecurityWebFiltersOrder.AUTHENTICATION);//Security的安全配置ServerHttpSecurity.AuthorizeExchangeSpec authorizeExchange = http.authorizeExchange();//加上授权的访问地址if (securityProperties.getAuth().getHttpUrls().length > 0) {authorizeExchange.pathMatchers(securityProperties.getAuth().getHttpUrls()).authenticated();}//加入忽略的访问地址if (securityProperties.getIgnore().getUrls().length > 0) {authorizeExchange.pathMatchers(securityProperties.getIgnore().getUrls()).permitAll();}authorizeExchange.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS).permitAll().anyExchange()// 任何资源除了忽略与认证可访问的外,都是需要进行授权判断才能放行,放行的认证处理器为permissionAuthManager.access(permissionAuthManager).and().exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(new JsonAccessDeniedHandler()).authenticationEntryPoint(entryPoint).and().headers().frameOptions().disable().and().httpBasic().disable().csrf().disable();return http.build();}}
【说明】
AuthenticationWebFilter为平台的对需要授权认证的地址的拦截器,平台的URL授权自定义的认证实现即是基于其内部的认证处理器customAuthenticationManager,令牌的处理器为tokenAuthenticationConverter
平台的访问认证及资源授权原理
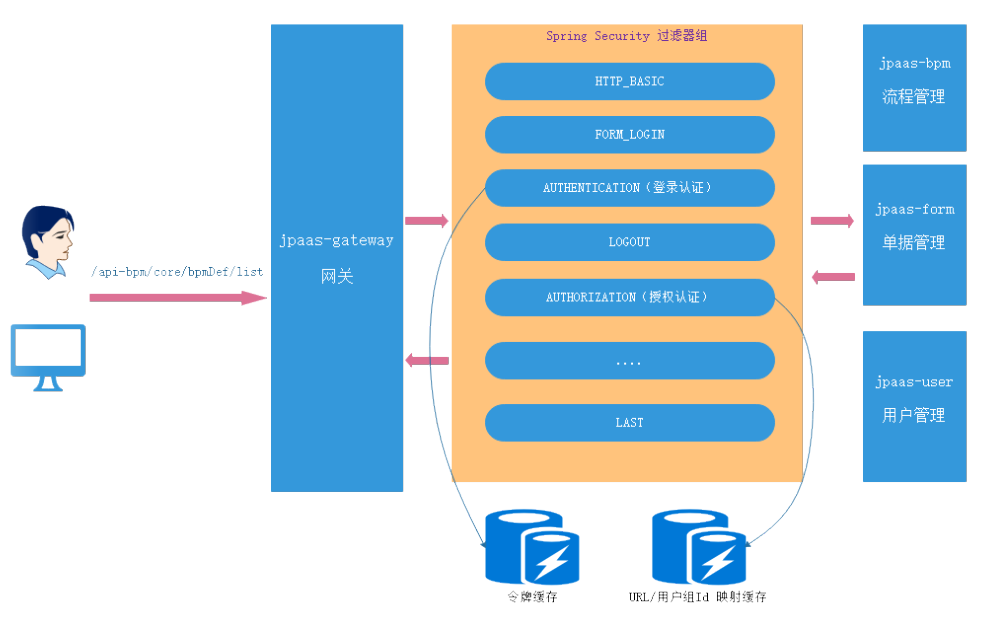
登录判断
AUTHENTICATION(登录认证)表示平台如何判断用户是否登录了,其是通过AuthenticationWebFilter来实现的。
而AuthenticationWebFilter则借助customAuthenticationManager来判断当前用户是否登录认证。因此只需要了解关注customAuthenticationManager的实现即可。
customAuthenticationManager的实现方法如下所示:
package com.redxun.gateway.auth;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.security.authentication.ReactiveAuthenticationManager;import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.OAuth2AccessToken;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.common.exceptions.InvalidTokenException;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.TokenStore;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.resource.BearerTokenAuthenticationToken;import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;/*** 用于进行网关的用户登录认证判断* @author yjy* @date 2019/10/6* <p>*/@Slf4jpublic class CustomAuthenticationManager implements ReactiveAuthenticationManager {private TokenStore tokenStore;public CustomAuthenticationManager(TokenStore tokenStore) {this.tokenStore = tokenStore;}@Overridepublic Mono<Authentication> authenticate(Authentication authentication) {return Mono.justOrEmpty(authentication).filter(a -> a instanceof BearerTokenAuthenticationToken) // 平台登录时,使用了该类型的令牌实现.cast(BearerTokenAuthenticationToken.class).map(BearerTokenAuthenticationToken::getToken).flatMap((accessTokenValue -> {//从缓存中读取该令牌OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = tokenStore.readAccessToken(accessTokenValue);//无令牌则表示没有登录或令牌已经失效if (accessToken == null) {return Mono.error(new InvalidTokenException("tokenInvalid"));} else if (accessToken.isExpired()) {//令牌过期则需要从缓存中移除tokenStore.removeAccessToken(accessToken);return Mono.error(new InvalidTokenException("tokenExpried"));}// 从令牌中获取认证对象OAuth2Authentication result = tokenStore.readAuthentication(accessToken);// 检查是否已经认证了if (result == null || !result.isAuthenticated()) {return Mono.error(new InvalidTokenException("tokenInvalid"));}return Mono.just(result);})).cast(Authentication.class);}}
url 拦截认证
在以上配置中有一块是以下代码的配置,表示访问的任何URL是需要认证访问:
authorizeExchange.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS).permitAll().anyExchange()// 任何资源除了忽略与认证可访问的外,都是需要进行授权判断才能放行,放行的认证处理器为permissionAuthManager.access(permissionAuthManager)
因此我们只需要了解permissionAuthManager是如何判断url的是合法访问即可。
/*** url拦截权限认证** @author yjy* @author csx* @date 2019/10/6* <p>*/@Slf4j@Componentpublic class PermissionAuthManager extends DefaultPermissionServiceImpl implements ReactiveAuthorizationManager<AuthorizationContext> {/*** 构建URL_GROUP映射*/public static final String apiUrlGroup = "apiMap_";@Resourceprivate RemoteApiService remoteApiService;@Overridepublic Mono<AuthorizationDecision> check(Mono<Authentication> authentication, AuthorizationContext authorizationContext) {return authentication.map(auth -> {ServerWebExchange exchange = authorizationContext.getExchange();ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();//检查当前的认证对象是否具有当前访问路径的访问权限boolean isPermission = super.hasPermission(auth, request.getMethodValue(), request.getURI().getPath());return new AuthorizationDecision(isPermission);}).defaultIfEmpty(new AuthorizationDecision(false));}/*** 获取URL与用户组Id的映射,并且放置于缓存中* @return*/@Overridepublic Map<String, Set<String>> selectApisByGroupIdsAndRedis(){Map<String, Set<String>> menuMap=(Map<String, Set<String>>) CacheUtil.get("api",apiUrlGroup);if(menuMap==null){menuMap = remoteApiService.getUrlGroupIdMap();CacheUtil.set("api",apiUrlGroup,menuMap);}return menuMap;}}
【说明】
以上的DefaultPermissionServiceImpl类的hasPermission为关键判断,原理比较简单,就是判断在缓存中URL-Group的映射中找到该URL对应的用户组Id,与当前登录的用户所属的用户组(如部门、岗位、职务等)匹配对比,若存在,则表示可授权访问。为了实现这个业务逻辑,平台需要在用户组与资源映射上做一些数据结构的逻辑处理。
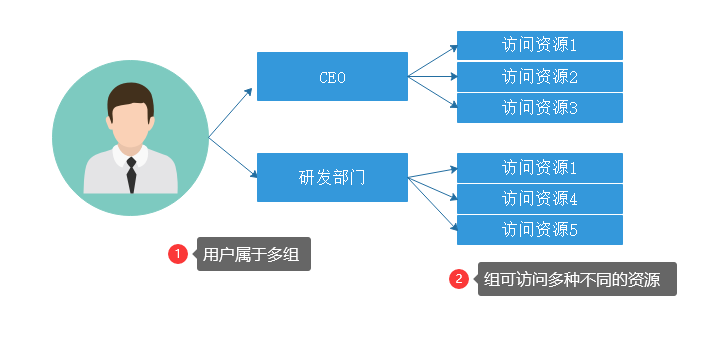
平台的安全管理是基于组的权限授权策略,即平台是对组进行授权的,组包括: 机构类型,用户类型,角色,职务,部门或其他组授权,而用户可分别属于多个不同的组。用户在登录时,即会根据其所在的组进行所有的权限合并,从而决定用户可访问的系统资源有哪些。其关系如下所示: